
BOILLAT Julien
Osteopat D.O/M.R.O.DK
Master Degree in Osteopathy (Switzerland)
Master Thesis in Cranial Therapy
Specialization in treatments of babies and kids
Auth. osteopath & Member of Danske Osteopater
Inflammation
What is inflammation?
Inflammation is a natural reaction of our immune system which gets activated because of inner or outer traumas.
It is a reparation process that stimulates blood vessels to dilate and therefore increase the amount of blood in the damaged tissues. Because blood is carrying all the cells and elements that the body needs for repairing, inflammation is a necessary physiological process that happens in all organisms.
But if it's natural, why is it painful?
Why do we take anti-inflammatory pills?
To increase blood circulation, the inflammation creates what we call a "vasodilatation". Vasodilatation is when the vessels get wider and are increasing their diameter. The vessel wall (or adventis) contains numbers of sensitive nerves. When the adventis is being pushed by the increased pressure, these sensitive nerves are stimulated and send the "pain" information to the brain.
This whole process is a mechanism for protection!
First the body repairs itself by sending more blood and then the brain, because of the pain, is aware to avoid certain movements that would impede the healing process.
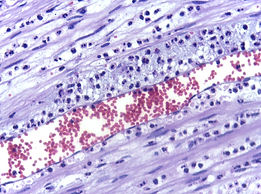
This image shows the dilatation of the blood vessel and the increase of the blood cells coming to repair the damaged tissue.
Well, like in any auto-immune reaction, sometimes the body cannot control the process so well and inflammation itself starts to be problematic and too painful.
This is where we start giving pills like Ibuprofen to try to calm down and break the circle of inflammation.
Remember, inflammation is a reparation mechanism and therefore, it is always advised to take Ibuprofen just before bedtime so that you are sure not to use the damaged structure during the effect of the medics.
How do I know if I have an inflammation?
The first and evident sign is pain, but this pain has very specific characteristics.
The first and most recognizable characteristic is the "resting pain". Inflammation tends to ease while the body is moving and warming up the muscle but when you go home and rest in the sofa, the pain starts to come and makes it difficult for you to start moving again. You could have an inflammation if you feel well during the daytime but after you go to sleep you start to wake up BECAUSE of the pain (and not because they are moving around in their bed).
Quite often my patients tell me: "Oh, I have morning pain, so is it an inflammation?"
People can fell stiffness and/or pain in the morning but if this pain disappear within approximately 30 minutes, then it is probably not an inflammation. If the pain persists for 2 hours after waking up, then the risk of an inflammation is quiet high.
Inflammation also has other symptom aspects such as swelling and feeling warm around the concerned area.
Food and inflammation
This is a subject that I am passionate about and I really like to talk about with my patients because food is an essential part of our everyday life and changing your diet can really relief many symptoms.
The chemistry behind it is very interesting but I will try to keep it simple here.
Most importantly, increased blood acidity creates inflammation processes. So inflammation or not, having acidic (low pH) blood is not good for anyone.
Acidity is protons (free molecules of Hydrogen - written H+ in chemistry). So the more H+ in your blood, the more acidic your blood will become.
And where do we find the most H+ in our food? Of course, in the things we enjoy to eat: SUGAR.
People then ask me: "So, I just need to stop eating candy and cakes?"
This is a good start but it's not enough. A lot of people associate "sugar" with "sweetness" which is of course true but there is a lot more food which contains a lot of protons without tasting sweet. We should rightly replace the term "sugar" by "carbohydrates" which are basically chains of Carbon associated with Oxygen and each of them covered by Hydrogen.
When the digested food enters your intestine, the elements are getting absorbed into your blood. The more carbohydrates your last meal contained, the more protons will pass into your blood which decreases the pH and thereby leads to micro-inflammations.
So next time you go shopping, check the description on the back of the packaging and see how many Carbohydrates per 100 gr you get. For an anti inflammatory diet, you should eat a maximum of 60 gr of carbohydrates per day but less would of course be even better!

This is glucose, a simple carbohydrate. All of them look the same, it is just the number of C that varies.
Can osteopathy help against inflammation?
Now you have understood that inflammation is a natural process inside the body so therefore we can not directly affect it or fix it. There is always a reason why there is an inflammation and this is where the holistic approach of osteopathy is efficient.
The osteopath will help you to identify the origin of the inflammation. Example: instead of taking Ibuprofen for weeks, why don't we just realign your pelvis so your sacrum stops compensating and stops pulling the musculoskeletal system of the lower back causing the inflammation? This is an example out of many others and it is a mechanical one.
Osteopathy always looks at a patient in three areas: the mechanical, the chemistry, the psychological.
All of them influence each other and pain can be due to the activation of any of them. For example, osteopaths very often come across shoulder inflammations (like the frozen shoulder) after a psychological trauma. Another example is a patient coming to me with sudden inflammatory pains after Christmas/New year due to all these protons they have adsorbed in these delicious but vicious Holiday meals.
